Montana State Legislature
Department of Administration
The Department of Administration provides services to state agencies, local governments, and Montana citizens in the following areas:
- Human resource management, workforce development, labor relations, and policy development • Information systems service hosting, telecommunications, 9-1-1 program management, tax revenue distribution to Public Safety Answering Points (PSAPS), data processing, public safety radio communications, and continuity planning
- Statewide information technology (IT) policies and standards development
- State financial institution oversight and regulation • Insurance procurement/administration and risk management services
- Property/casualty claims administration and tort litigation services • Accounting, financial reporting, warrant writing, and policy development
- State treasury services
- Federal Social Security Section 218 program administration
- State bonded indebtedness administration
- Capitol complex building and grounds maintenance and security
- Procurement and surplus property administration and policy development
- Printing, mail, and messenger services
- Technical assistance and training to local government accounting and financial personnel
- Audit review and enforcement for local governments
- Long-Range Building Program • State employee group benefits
- Workers’ compensation management The Board of Examiners, Burial Preservation Board, Information Technology Board, State Banking Board, State Board of County Printing, State Compensation Insurance Board (Montana State Fund), State Tax Appeal Board, Office of the State Public Defender, Public Employee Retirement Board, Teachers’ Retirement Board, and the Montana State Lottery are attached to the department for administrative purposes only.
The department’s budget consists of the following major programs and two administratively attached agencies with the following functions:
Director's Office – provides the overall supervision and coordination of agency programs. The office provides legal, IT management, financial, budgeting, accounting, human resource management, and payroll services for the department and some of its attached agencies. The Offices of Labor Relations represents the Governor’s Office in all matters relating to collective bargaining and Continuity and Emergency Management provides oversight and management in case of a catastrophic event.
Governor-Elect – provides the Governor-elect and necessary staff with office space in the capitol complex, as well as furnishings, supplies, equipment, and telephone service for the period between the general election and the inauguration. The program is funded only for one year every other biennium.
State Financial Services Division – performs many centralized functions and administers state and federal programs to state agencies, local government entities, and Montana citizens and businesses. The division consists of four bureaus – Statewide Accounting, State Procurement, SABHRS Financial Services Technology Bureau and Local Government Services. The Division prepares and publishes the state’s annual comprehensive financial report (CAFR), maintains a statewide accounting structure, performs central banking functions, and maintains accountability of all money and securities belonging to or held in trust by the state. The Division manages the state payment processes and state vendor file. The Division works with local governments (counties, cities & towns, school districts, and special districts) to support uniform financial accountability, and to assist the local governments in complying with their statutory, financial, and budgetary reporting requirements, including provisions of the Montana Single Audit Act. The State Social Security Administration is housed within Local Government Srevices and is responsible for administering Section 218 of the Social Security Act by providing education and outreach and insuring proper application of Social Security coverage to all state and local government employees. The Division also provides system support and maintenance of the state’s enterprise accounting, budgeting, and eProcurement systems as well as providing professional procurement services and oversight to all state agencies for the acquisition of goods and services as defined in the Montana Procurement Act (MCA Title 18-4). State Procurement establishes statewide contracts for commonly used goods, manages the state’s fuel and procurement card programs, and offers procurement/contract management training to state agencies.
Architecture and Engineering – manages remodeling and construction of state buildings. The division’s functions include: planning new projects and remodeling projects; advertising, bidding and awarding construction contracts; administering contracts with architects and contractors; disbursing building construction payments; and providing design services for small projects. The program also formulates a long-range building plan for legislative consideration, oversees the adoption of high-performance standards for state-owned buildings, and manages the statewide facility condition assessment process.
General Services Division – provides certain internal services to government agencies and the public through four program areas:
- Capitol Facilities Management (CFM) provides the following services for state agencies in the Capitol Complex (State owned buildings within a ten-mile radius of Helena) either directly or through the administration of service contracts: security, identification cards, access control, facilities repair, maintenance, construction, utilities, energy consumption monitoring, disaster response and recovery, space allocation, janitorial, pest control, grounds maintenance, recycling, and solid waste collection. CFM also manages public events on the Capitol campus.
- Real Property and Leasing (RPL) negotiates and manages leases for state agencies throughout the state. RPL manages 77.0% of all state leased space in Montana.
- State Print and Mail (SPM) provides print and mail services to state agencies. Services include internal and external (contracted) printing, marketing, managed print services, mail preparation, central mail operations, and interagency (deadhead) mail. SPM also operates the United States Post Office in the Capitol.
- Surplus Property and Recycling (SPR) manages both the state and federal surplus property programs, making surplus property services available to all city, county, and tribal governments in Montana. SPR also manages recycling contracts.
State Information Technology Services – establishes and enforces statewide information policies and standards and implements and optimizes shared information technology platforms and services such as the state network, state data centers, servers and storage, statewide local and long-distance telephone and video network services, and enterprise custom and commercial applications. The division provides disaster recovery capabilities furthering the state’s ability to efficiently and securely process data. In addition, the division manages the Public Safety Services Bureau including the state’s 911 and public safety communications programs; develops the statewide IT strategic plan and coordinates agency IT strategic plans; develops and oversees state IT standards and policies; and reviews and approves IT equipment and software acquisitions, including an IT project management office.
Banking and Financial Institutions – licenses, charters, supervises, regulates, and examines a variety of financial institutions operating in Montana. These institutions include: state-charted banks and trust companies; savings and loans and credit unions; consumer loan and sales finance companies; title loan companies; escrow companies; deferred deposit loan companies; and mortgage brokers, mortgage lenders, and mortgage loan originators.
Health Care and Benefits—administers employee benefit plans that include health, life, dental, prescription drugs, long-term disability, vision, flexible spending accounts, sick leave fund, employee assistance services, health promotion, and a voluntary employee benefit health care expense trust. The Workers’ Compensation Management Program provides a central resource for agencies in working to enhance safety, loss prevention, and return to work programs, and works with the workers’ compensation insurer to coordinate workers’ compensation coverage and policy management issues.
State Human Resources – provides state agencies with a variety of human resource management programs. These programs include: human resource rules, policies, and standards for the Executive Branch agencies; training and other professional development services to state agencies; the human resource portion of the Statewide Budgeting, Accounting and Human Resource Systems (SABHRS); and human resource information services, supplying payroll and other human resource information systems for all branches of state government.
Risk Management and Tort Defense – administers a comprehensive plan of property and casualty insurance protection on behalf of state agencies and universities. The division insures state agencies/universities against risk of loss related to aircraft, airports, boilers and machinery, cyber information security, fidelity bond, fine art, Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), professional liability, property, surety bond, and vehicles. In addition, the division provides risk management training, on-site hazard inspections, consulting services, and claims administration. The division also investigates, evaluates, and resolves property/casualty claims, and coordinates the adjudication and settlement of tort claims involving personal injury/property damage.
Attached-to Agencies in the DOA budget:
Montana State Lottery – designs, markets, and administers lottery games operating in Montana. The lottery presently offers a variety of instant/scratch and lotto-style games, some in cooperation with other lotteries through the Multi-State Lottery Association. The net revenue, up to approximately $12.4 million, is deposited in the state general fund on a quarterly basis, after prizes, sales commissions, and operating expenses are taken out. Any net revenue above this amount is required to be transferred to the STEM scholarship account.
State Tax Appeal Board – provides a tax appeal system for all actions of the Department of Revenue. The Board hears appeals from decisions of the 56 county tax appeal boards and takes original jurisdiction in matters involving income taxes, corporate taxes, severance taxes, centrally assessed property and new industry property, motor fuel taxes, vehicle taxes, and cabin site leases.
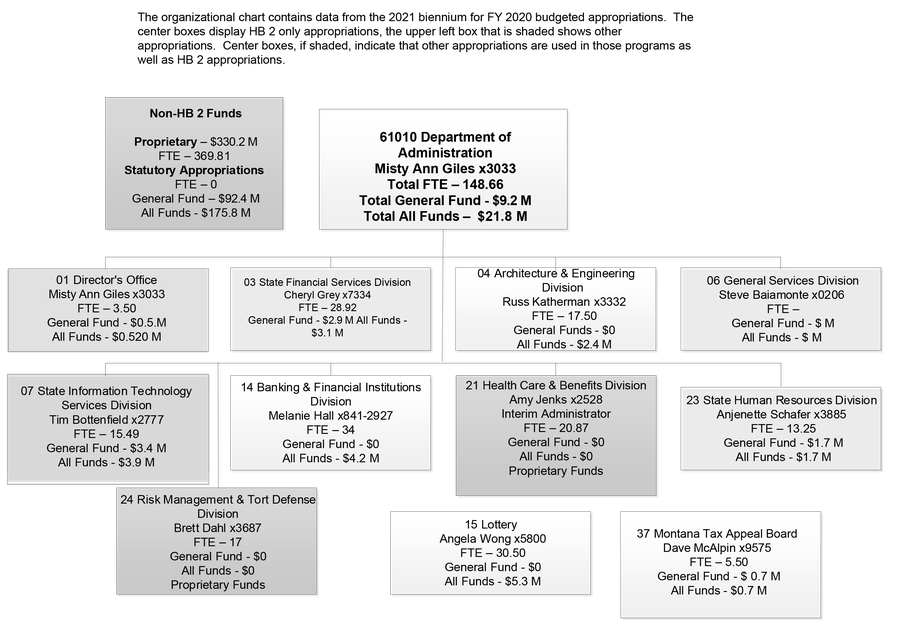
Below is an organizational chart of the department, including full-time employee (FTE) numbers and the HB 2 general fund appropriations and the total of all funds. Unless otherwise noted, all phone extensions are preceded by (406) 444.
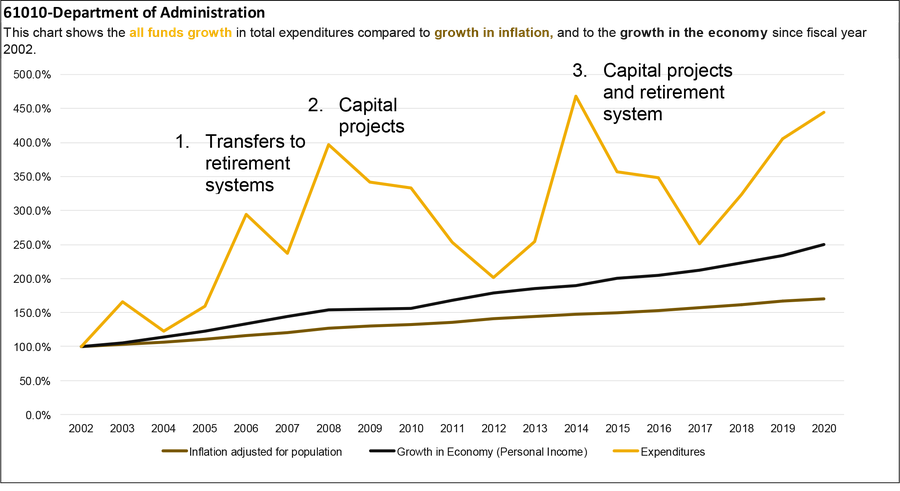
This report includes a series of charts that compare expenditure growth to the growth in the economy and growth in inflation adjusted for population. Montana statute, 17-8-106, MCA, recommends using growth in personal income for comparison purposes. Personal income is a measure for growth in the economy. Comparing growth allows financial planners to consider past and future demands in services or changes in revenues.
Overall, there is significant volatility in expenditures from all governmental funds when compared to inflation and growth in the economy. This volatility is primarily due to an increase in transfers and local assistance to the retirement systems and capital projects. The following list discusses in more detail the inflection points on the charts:
- HB 1 (2005 December Special Session) transferred $100.0 million from the general fund to the teachers’ retirement system pension trust fund and $25.0 million from the general fund to the public employees’ retirement system pension trust fund
- HB 4 (2007 May Special Session) transferred $77.4 million from the general fund to capital projects
- The 2013 Legislature approved general fund transfers of $101.2 million. These transfers were primarily related to the long-range building program (HB 5), renewable resources grant (HB 6), long-range information technology (HB 10), treasure state endowment program (HB 11). Additionally, the legislature passed HB 377 which increased general fund contributions to the teachers’ retirement system by $25.0 million and HB 454 which increased transfers to the public employees’ retirement system by $21.0 million

- Between FY 2008 and FY 2012 there was a general decline in general fund transfers
- In FY 2017 state special revenue increased because the legislature approved transfers to the general fund in HB 6 (2017 November Special Session). These transfers primarily were from the following state special revenue funds: treasure state endowment, school facility and technology account, big sky economic development program, and the accommodation tax account
- In FY 2019 general fund transfers increased because of transfers to the budget stabilization reserve fund
Legislative Changes
2019 Legislature
- The legislature passed HB 725, which authorized sports wagering in Montana. The Montana State Lottery operates the sports wagering platform.
- The legislature passed SB 60, which revised laws related to financial aid and changed how the STEM scholarships receive funding. Net revenue from the Montana State Lottery is first transferred to the Montana STEM scholarship fund (starting in FY 2020). The amount remaining after the distribution to the scholarship fund is deposited into the state general fund.
2017 Legislature
- The legislature passed HB 209, which increased the percentage of coal severance taxes directed to the Coal Board from 2.9% to 5.8% which reduced the general fund available for transfer to the Public Employees Retirement System (PERS). The Legislature offset the reduction to PERS within the Department of Administrations budget by providing for a state supplemental transfer of $1.6 million in FY 2018 and $1.7 million in FY 2019
- The legislature passed HB 61, which revised and updated 911 laws including requiring $5.4 million of enhanced 911 funding to be transferred to a new state special revenue account for next generation 911 services, 911 geographical information system mapping, and statewide planning
2013 Legislature
- The legislature passed HB 377 and HB 454, which increased employer and employee contribution rates for certain public employee retirements plans and provided for additional transfers from the general fund to improve the solvency of the trusts
2011 Legislature
- The legislature passed HB 90, which required the licensure and regulation of residential mortgage loan servicers
- The legislature passed HB 53, which raised the age that dependents may remain covered under their parents’ state employee group health insurance from 25 to 26. The change was made to comply with the federal Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010
Click the double-sided arrow in the lower right corner of the image below to enlarge the graphic. Then, click the box next to the agency you want to see. To minimize, click Esc.
Legislative Studies
State Administration & Veteran's Affairs Interim Committee work
Audit Reports
Information Systems Audit - Governance Practices for Information Technology Investments - Jan 2018
Performance Audit - Administration of State Procurement and Contract Management - Nov 2018
Financial Compliance Audit - Department of Administration - Nov 2018
Information Systems Audit - Lottery Security - Sept 2018
Performance Audit - Oversight of State Agency Procurement Card Use - May 2019
Employee Group Benefits Claim Audit - April 2020
Legislation:
HB 277, Provide for a state government performance and results act
HB 484, Require state programs to participate in a health information exchange
HB 509, Revising robocall fines
SB 287, Revise public project financing laws
SB 308, Revise the Montana Building and Loan Associations Act
SB 309, Revising state lottery laws relating to compensation of lottery employees
SB 369, Generally revise laws related to insurance coverage of telemedicine services
HB 615, Revise tax increment financing laws related to bonding
HB 616, Revise laws related to the adoption of a tax increment provision
Gov. Gianforte 2023 Biennium Budget - Department of Administration
2023 Biennium Executive Summary - Department of Administration
Jan. 7 Budget
Nov. 15 Budget
Department of Administration Summary
- 01-Director's Office
- 03-State Financial Services Division
- 04-Architecture & Engineering Program
- 06-General Services Division
- 07-State Information Technology Division
- 14-Banking & Financial Institutions Division
- 15-Montana State Lottery
- 21-Health Care & Benefits Division
- 23-State Human Resources Division
- 24-Risk Management & Tort Defense
- 37-Montana Tax Appeal Board
Agency profile information provided by the Legislative Fiscal Division.
