Montana State Legislature
Department of Agriculture
The Department of Agriculture (Agriculture) regulates and promotes agriculture and associated industry in Montana. Agriculture is one of only two agencies required under the Montana Constitution and must “protect, enhance, and develop all agriculture” (Article XII, Section 1). Due to the existence of the Department of Livestock, Agriculture focuses primarily on non-animal related farm products.
Three divisions form Agriculture and perform the following functions:
- The Central Services Division provides managerial and administrative support services to the entire department.
- The Agricultural Science Division regulates, certifies, researches, inspects, registers, and licenses items related to environmental and consumer protection in agriculture. The division also oversees grants to counties for noxious weeds.
- The Agricultural Development Division focuses on growth and expansion of Montana agriculture, including rural development, wheat and barley promotion, agriculture marketing, and the state grain laboratory
Below is an organizational chart of Agriculture, including full-time equivalent (FTE) numbers and the HB 2 base general fund appropriations and the total of all funds. Unless otherwise noted, all phone extensions are preceded by (406) 444.

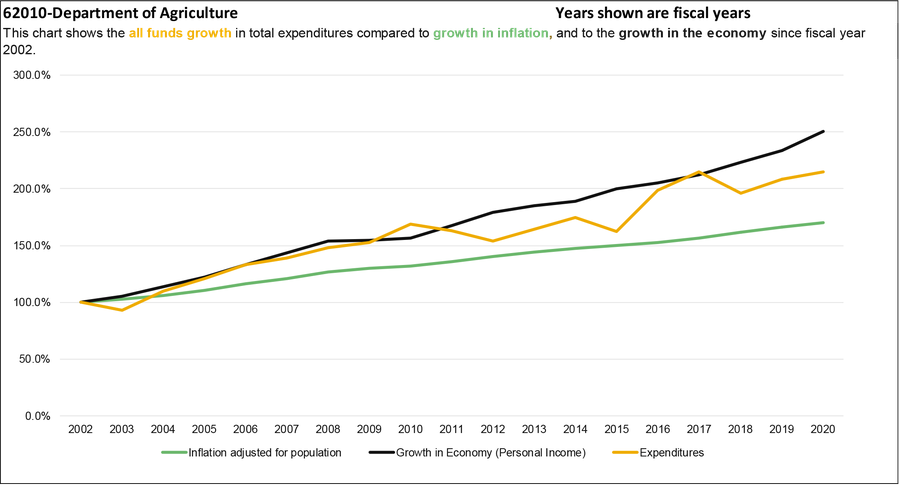
This report includes a series of charts that compare expenditure growth to the growth in the economy and growth in inflation adjusted for population. Montana statute, 17-8-106, MCA, recommends using growth in personal income for comparison purposes. Personal income is a measure for growth in the economy. Comparing growth allows financial planners to consider past and future demands in services or changes in revenues.
HB 2 authority funds 81.1% of total expenditures. The HB 2 base budget has grown from $8.1 million in the 2001 biennium to $17.8 million in the 2021 biennium, an annual growth rate of 4.2% compared to a rate of inflation of 2.1% over the same period.
Personal services expenses have grown at an annual rate of 4.4% between FY 2002 and FY 2018. Growth is due to an increase in FTE from 109.55 FTE in FY 2002 to 114.42 FTE in FY 2018. Total expenditures have almost doubled from $3.6 million to $7.1 million over the 16-year period. Growth in employee pay is a combination of an increase in FTE and increases in wages and salaries. Employee benefits is the fastest growing component of personal services, growing at an annual rate of 6.9%. Total expenditures for benefits account for $1.2 million or about one third of total increases in personal services.
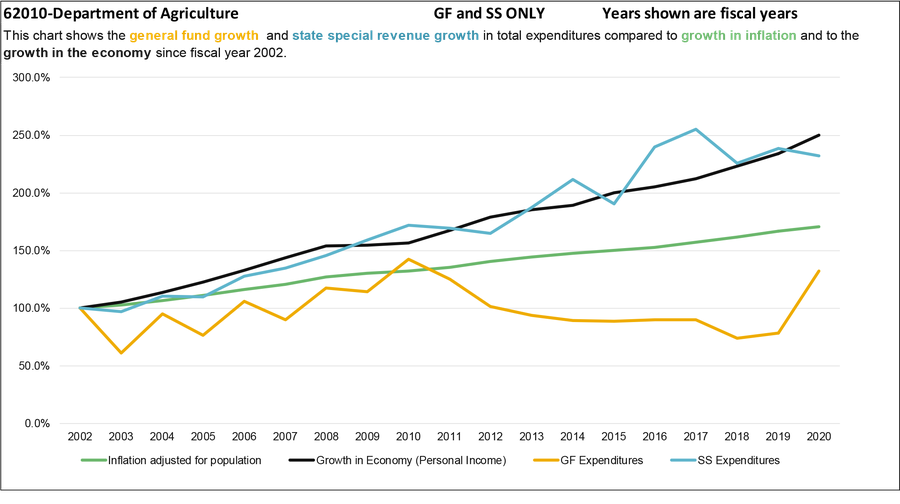
As shown in the chart above, the agency has seen a shift in expenditures away from the general fund to state special revenue sources since the 2003 biennium. Expenditures from state special revenue has increased as a percentage of total expenditures from 70.4% to 79.2%.
Legislative Changes
2019 Session
- HB 151 increases the maximum amount of the wheat and barley check-off, however any change in the current assessment would require action by the Wheat and Barley Committee and a rule change by the Department of Agriculture.
- HB 52 extends the sunset date on the Cooperative Development Center and the Growth Through Agriculture programs to June 30, 2027 and increases the appropriation of the Coal Severance Tax interest to these programs.
- HB 443 creates a new requirement that hobbyist beekeepers register with the Department of Agriculture, administrative costs will be covered by fees charged by the agency.
- SB 176 allows the agency to implement a state hemp certification program. The agency may collect fees to offset the administrative costs of the program.
2015 Session
- SB 78 eliminated the Mint Committee and the need for the department to administratively support it.
- HB 105 allowed the department to set fees for analytic lab services. Fees collected are placed in a state special revenue fund for the costs of the services.
2013 Session
- HB 189 increased the maximum amount of hail insurance per acre of crops and would be phased in by the Department of Agriculture over two years. The legislation reduced the collection fee percentage paid to the Department of Revenue and capped the transfer to the general fund.
- SB 144 changed the amount the department may spend to manage the noxious weed management program. This reduced the amount spent on department-based programs and increased the amount distributed as grants.
2011 Session
- HB 621 revised the Aquatic Invasive Species act and provided funding to the department.
2009 Session
- SB 343 established the Montana Aquatic Invasive Species Act, requiring the department to establish a mechanism for Montana to take concerted action to detect, control, and manage invasive species to prevent further introduction, importation, and infestation.
Click the double-sided arrow in the lower right corner of the image below to enlarge the graphic. Then, click the box next to the agency you want to see. To minimize, click Esc.
Legislative Studies
Economic Affairs Interim Committee work
Audit Reports
Financial Compliance Audit - Department of Agriculture - May 2020
Legislation
See the Legislation tab on the Economic Affairs Interim Committee web page
HB 294, Revise fees for agricultural seed licenses
HB 390, Revise laws related to agricultural equipment repair
HB 396, Clarify hemp seed as commercial feed
SJ 7, Remove Hidden Pasture Creek from WSA
SB 199, Montana Local Food Choice Act
SB 211, Revise local subdivision review criteria regarding agriculture
HB 367, Revise constitutional language regarding harvest heritage
HB 361, Revise agriculture license requirements laws
HB 410, Pollinator Protection Act
SB 270, Revise valuation of commodities on state lands
SB 273, Revise laws related to agricultural equipment repair
Agency profile information provided by the Legislative Fiscal Division.
