Montana State Legislature
Department of Military Affairs
The Department of Military Affairs (DMA) has three primary components to its mission:
- Federal – Serve as the primary federal reserve force in support of the national security objectives when called upon by the President of the United States
- State – Protect life, property, preserve peace, order, and public safety for Montana’s citizens, when called upon by the Governor
- Community – Participate in local, state, and national programs that add value to America The Department of Military Affairs, administered by the Adjutant General, oversees activities of the Air and Army National Guard, Disaster and Emergency Services, and the National Guard Youth ChalleNGe program. The Montana Board of Veterans' Affairs is administratively attached to the department. Services provided within DMA include:
- Providing trained and equipped military units for use in the event of state or federal mobilization • Maintaining numerous military facilities in Montana and planning and contracting for construction of military facilities and training areas
- Providing statewide communication services, security contracts, and leases for buildings and land used by the Army National Guard
- Providing trained and equipped military air units for use in event of state or federal mobilization, including wildfire support
- Providing statewide disaster planning and preparedness activities and coordination of federal, state, and volunteer assistance to communities, local and tribal governments in the event of an incident, emergency, or disaster
- Assisting discharged veterans and their families regarding veteran benefits and administering three veteran cemeteries located in Montana. The Board of Veterans’ Affairs is administratively attached to the Department of Military Affairs
- Providing scholarship awards to enlisted Montana National Guard troops enrolled as full-time undergraduate students in colleges, universities, or training programs
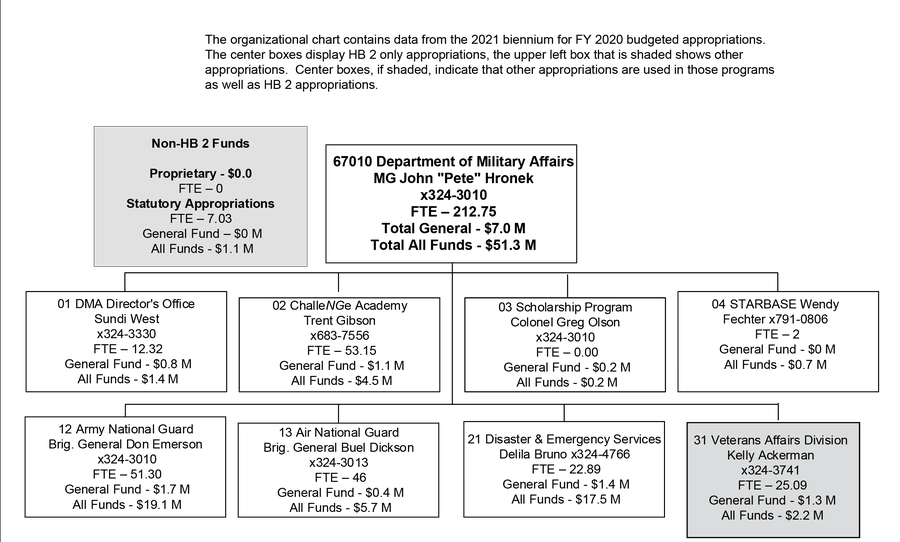
Below is an organizational chart of DMA, including full-time employee (FTE) numbers and the HB 2 general fund expenditures and the total expenditures from all funds. Unless otherwise noted, all phone extensions are preceded by (406) 444.
This report includes a series of charts that compare expenditure growth to the growth in the economy and growth in inflation adjusted for population. Montana statute, 17-8-106, MCA, recommends using growth in personal income for comparison purposes. Personal income is a measure for growth in the economy. Comparing growth allows financial planners to consider past and future demands in services or changes in revenues.
The Department of Military Affair’s (DMA) budget consists primarily of federal special revenue funds, with small amounts of general fund, state special revenue, and capital projects funding. The volatility in all funds expenditures within DMA is primarily related to surges in federal funds for disaster relief and pre-disaster mitigation grants, as well as federal funds for major capital construction projects such as new armories or readiness centers. Excluding these funds, the trend in expenditures for DMA generally parallels with inflation and population. The following list discusses in more detail the inflection points on the charts:
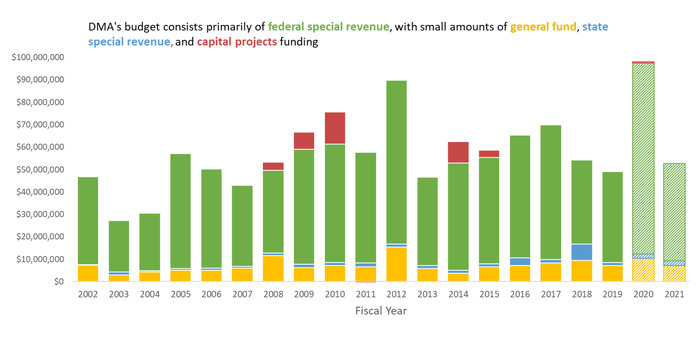
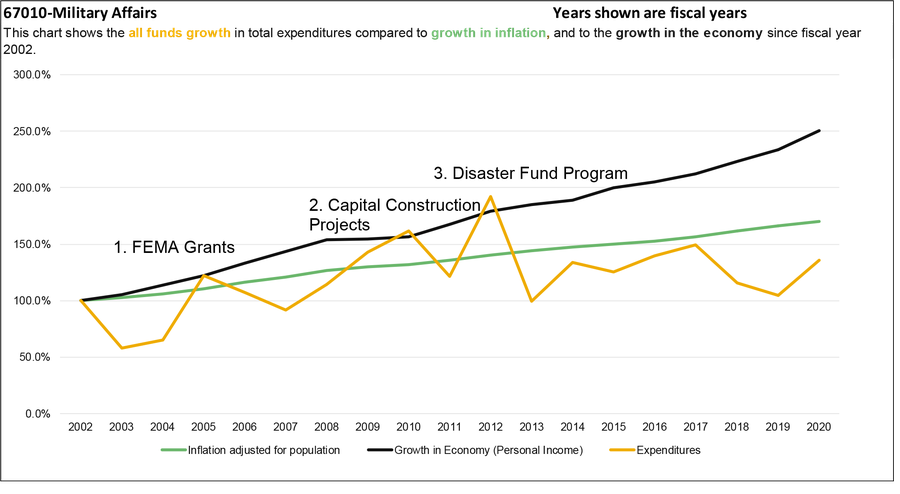
1. In FY 2005, the Disaster and Emergency Services Program received federal grants from the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) for pre-disaster mitigation plans, hazard assessment, emergency response preparation, and other federal grants for terrorism preparedness.
2. In FY 2005, the Military Capital Construction Program expended funds for the construction of several new armories. From FY 2007 through FY 2010, expenditures increased for the construction of the Armed Forces Reserve Center in Missoula and various other military construction projects. In FY 2014 and FY 2017, the program expended funds for the construction of readiness centers.
3. In FY 2012, expenditures from the Disaster Fund Program totaled $50.9 million, $49.3 million of which was a statutorily appropriated presidential FEMA grant related to severe storms and flooding Montana experienced in 2011.
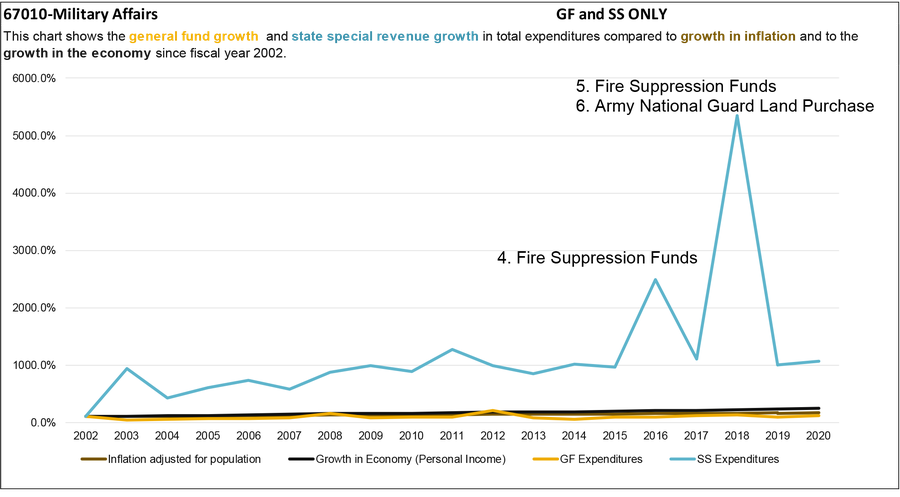
4. In FY 2016, the Disaster Fund Program expended approximately $2.1 million from the fire suppression state special revenue fund related to the 2015 fire season.
5. In FY 2018, the Disaster and Emergency Services Division expended approximately $3.9 million from the fire suppression state special revenue fund related to the 2017 fire season.
6. Additionally in FY 2018, the Army National Guard Program expended approximately $1.6 million in statutory authority from the land purchase state special revenue account.
General fund
General fund supports a portion of most of the programs in DMA and the entire cost of the National Guard Scholarship Program. General fund is primarily used to meet the state match requirements for federal funds
in the Army and Air National Guard Programs and the Disaster and Emergency Services Division. General fund expenditures for DMA have grown at a similar rate to population and inflation.
State special revenue
State special revenue is predominately expended in the Disaster and Emergency Services Division and Veterans’ Affairs Program. Veterans’ Affairs accounts for the majority of the state special revenue funding with revenues generated through vehicle registrations, specialty license plates, and donations. Disaster and Emergency Services generally has a small amount of state special revenue expenditures for training and search and rescue operations. DMA has received a small amount of funding from the fire suppression state special revenue account for disaster-related expenditures; however, the Department of Natural Resources and Conservation expends a majority of the funds for fire suppression through their programs.
Click the double-sided arrow in the lower right corner of the image below to enlarge the graphic. Then, click the box next to the agency you want to see. To minimize, click Esc.
Legislative Studies
State Administration and Veteran's Affairs Interim Committee work
Audit Reports
Financial Compliance Audit - Department of Military Affairs - Oct 2019
State Administration & Veteran's Affairs Interim Committee web page
Legislation:
HB 362, Clarify credit for military leave during employment
HB 491, Revise access to military discharge records
HB 522, Create the Montana military strategic and economic task force
HB 590, Clarify military access to federal leave of absence
Gov. Gianforte 2023 Biennium Budget - Department of Military Affairs
2023 Biennium Executive Summary - Department of Military Affairs
Agency profile information is provided by the Legislative Fiscal Division.
